Table of Contents
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a crucial role in the medical field, safeguarding healthcare workers and patients alike. From masks to gloves, each item serves as a vital barrier against potential health hazards. Among these essential protective measures, gowns stand out as a critical component in maintaining safety and hygiene standards in healthcare settings. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between two types of medical gowns: isolation gown vs surgical gown. By exploring the key differences between these protective garments, we’ll help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about which type of gown is most appropriate for various medical scenarios(Medline). Our in-depth analysis of “Isolation Gown vs Surgical Gown” will cover their specific uses, materials, and regulatory standards, equipping readers with the knowledge needed to enhance workplace safety and patient care.
Definition and Purpose: Isolation Gown Vs Surgical Gown
Isolation gowns and surgical gowns serve distinct purposes in healthcare settings.
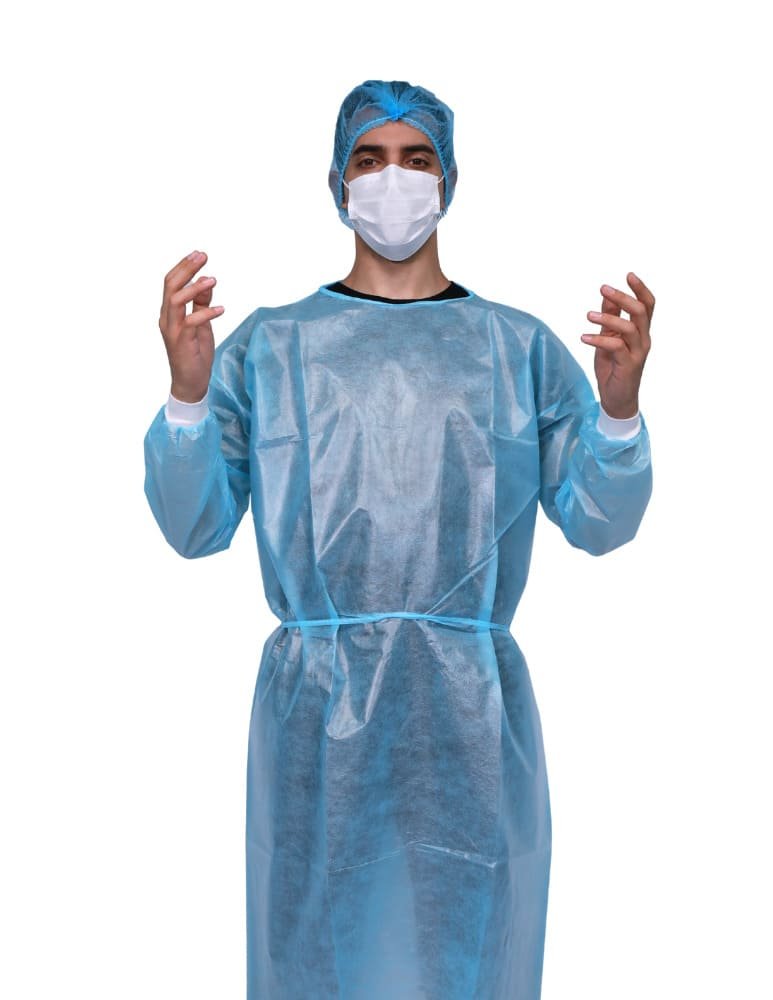
Isolation gowns, provide a barrier against low to moderate-risk contamination. They are disposable, cost-effective, and widely used in hospitals and clinics for routine patient care, especially when dealing with infectious diseases. (FDA)
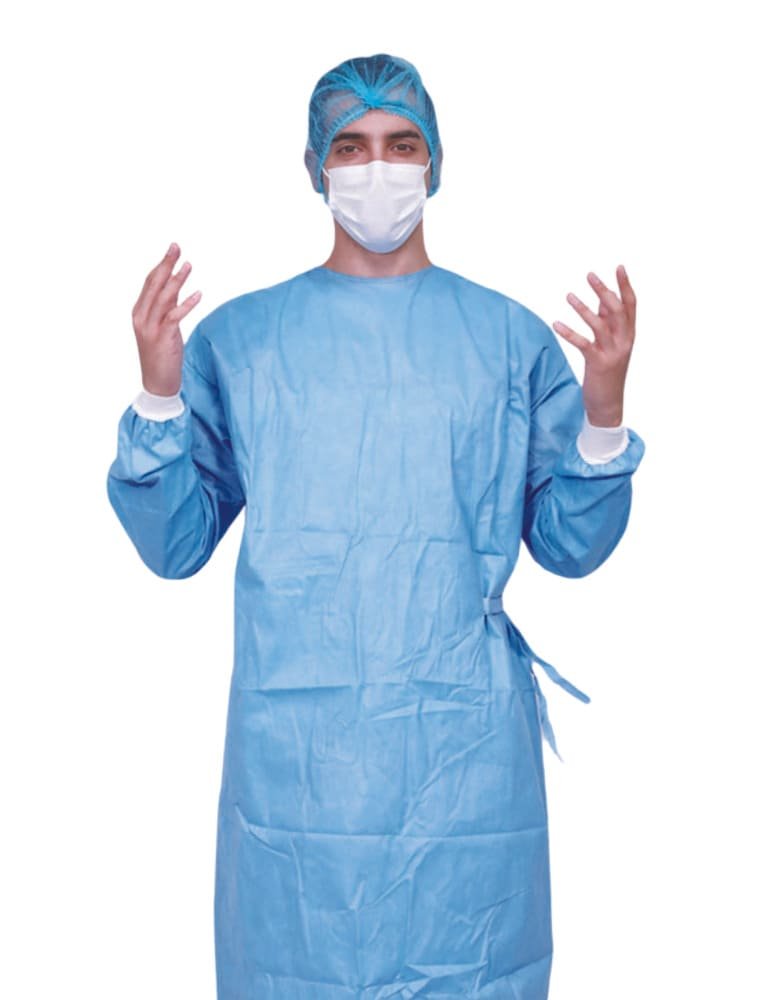
Surgical gowns, on the other hand, offer a higher level of protection and are crucial for maintaining sterile environments during surgical procedures. Surgical gowns are designed to resist liquid penetration and microbial transfer, which are essential in operating rooms where maintaining a sterile field is critical for patient safety.
Key Differences: Isolation Gown Vs Surgical Gown
Material & Fabric
Surgical gowns and isolation gowns differ primarily in material composition and fabric weight.
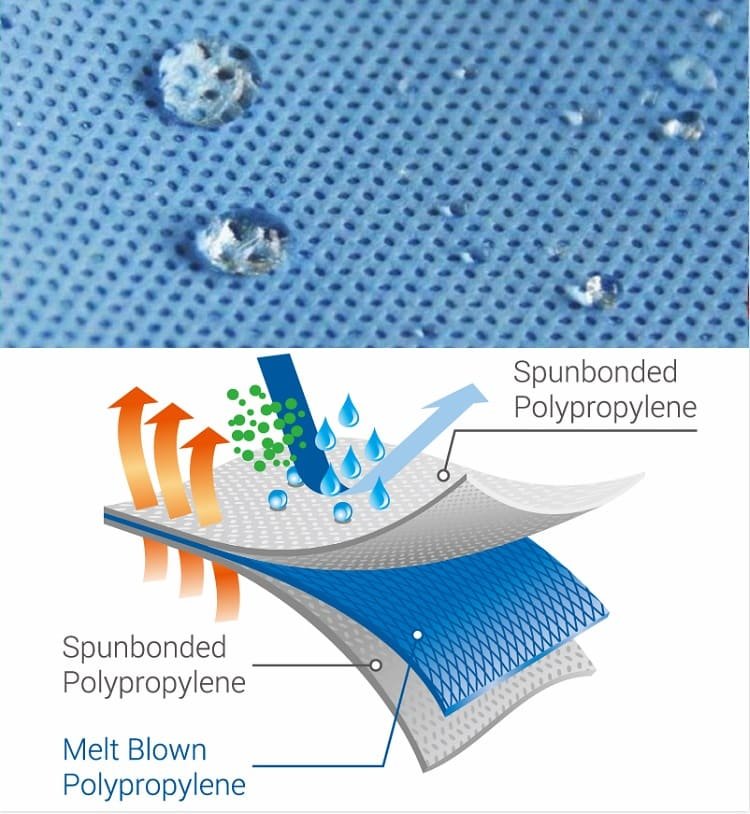
Surgical gowns, designed for high-risk environments, typically use non-woven synthetic materials like SMS or SMMS, sometimes incorporating polyethylene films. These gowns feature thicker fabrics (35-55 gsm) and correspond to AAMI Levels 3-4, providing maximum barrier protection.

Isolation gowns, intended for less intensive settings, are lighter (20-40 gsm) and often made from non-woven materials like polypropylene, SMS, or polyethylene-coated non-woven material, providing a barrier against low to moderate-risk contamination. They usually align with AAMI Levels 1-2, offering adequate protection for routine healthcare scenarios. Understanding these distinctions ensures appropriate gown selection based on protection requirements and comfort needs.
Design & Style: Isolation Gown Vs Surgical Gown
Critical Zones
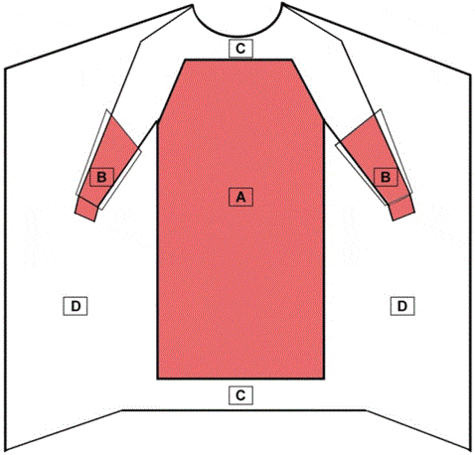
Surgical gowns feature specific critical zones requiring the highest protection, primarily the front from shoulders to knees and arms from wrists to above elbows. These gowns often include reinforced areas in critical zones and 4 ties at the waist, designed for a snug fit to ensure stability during procedures. The back is typically non-protective. Surgical gowns prioritize comprehensive coverage and protection in specific areas crucial for surgical settings.
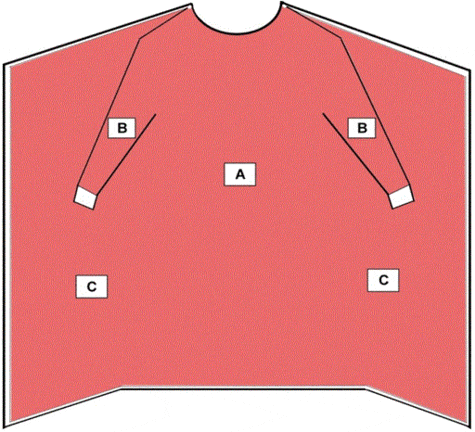
In contrast, isolation gowns consider the entire garment a critical zone (PMCID: PMC4791533), except for bindings, cuffs, and hems. They generally lack reinforced areas, as they’re not intended for high-risk surgical procedures. Isolation gowns cover as much of the body as possible while providing a looser fit for ease of movement and donning/doffing. This design reflects their purpose in general healthcare settings where full-body protection is needed.
Closure
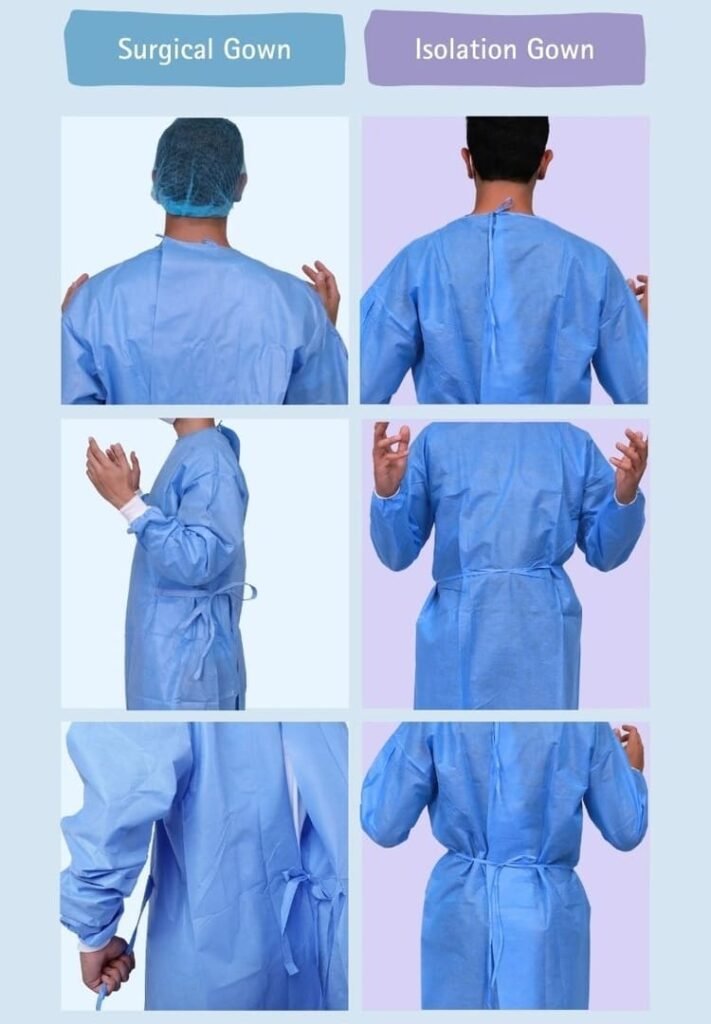
- Surgical Gowns: Typically feature secure closures at the back, waist, and neck. At the neck, there is a longer Velcro or two ties, at the waist there are 4 ties at the back to ensure a secure closure.
- Isolation Gowns: For cost considerations, customers usually choose a tie-on collar or a shorter Velcro. And, at the waist, there are two ties to ensure proper fastening at the back.
Cuffs
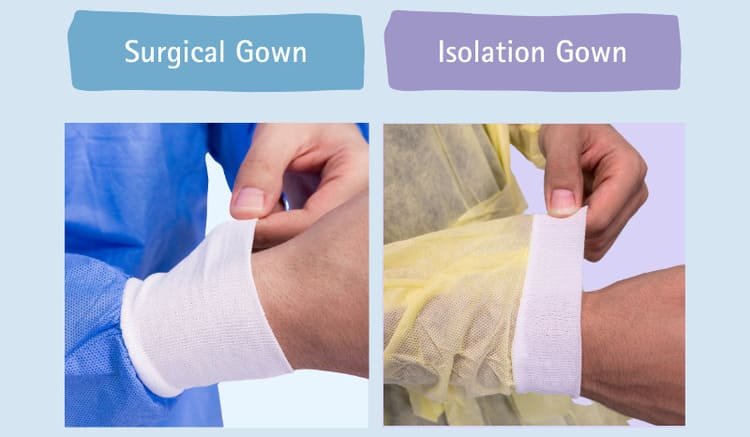
- Surgical Gowns: Surgical gowns usually have knitted cuffs made of polyester or cotton. Cuffs are designed to be tight-fitting to maintain sterility. Surgical gown cuff length is much longer than isolation gowns, usually 7-10cm long, to ensure tight-fitting.
- Isolation Gowns: Unlike surgical gowns, isolation gowns have two types of cuff choices, elastic or knitted cuffs. The cuffs are generally looser-fitting compared to surgical gowns. Some isolation gowns may have thumb loops for added security.
Size
- Surgical Gowns: Often come in a variety of sizes to ensure a proper fit for different body types. The fit is crucial to maintain sterility and comfort during long procedures.
- Isolation Gowns: Usually have a more universal fit, designed to be worn over regular clothing. They are often looser to accommodate different body sizes and to be quickly put on and taken off.
Color
- Surgical Gowns: Typically come in standard colors like blue or green, which are chosen for their calming effect and their ability to reduce glare under surgical lights.

- Isolation Gowns: Can come in a variety of colors, including yellow, blue, and white. The color can sometimes indicate the level of protection or the type of procedure for which the gown is intended.
Isolation gowns serve as a versatile first line of defense in lower-risk healthcare environments, offering protection against fluid penetration and contamination. These gowns are designed to provide a range of protection levels, from minimal to AAMI Level 1 and Level 2. The minimal protection level is suitable for basic care settings with little to no risk of fluid exposure.

AAMI Level 1 gowns
Offer slight fluid resistance, ideal for standard precautions and visitor use.

AAMI Level 2 gowns
Provide a higher degree of fluid resistance, making them suitable for low to moderate fluid exposure scenarios such as drawing blood or inserting IVs.
Surgical gowns, on the other hand, offer superior protection tailored for high-risk medical procedures and environments. These gowns are engineered to provide a robust barrier against fluid and microbial penetration, particularly in critical areas such as the chest and sleeves. Surgical gowns typically meet AAMI Level 3 or Level 4 standards, ensuring maximum safety during moderate to high-risk procedures.

AAMI Level 3 gowns
Offer moderate fluid resistance, suitable for arterial blood draws and trauma cases.

AAMI Level 4 gowns
provide the highest level of fluid and microbial protection, essential for long, intense procedures with high fluid exposure risks, such as orthopedic surgery or cesarean sections.
The enhanced protective capabilities of surgical gowns make them indispensable in operating rooms and other high-stakes medical settings where preventing cross-contamination is crucial.
Sterility
Surgical gowns are provided sterile(FDA), creating a vital barrier in surgical environments where contamination prevention is critical. Their fluid-resistant material protects against bodily fluids, minimizing infection risks.
Isolation gowns, typically non-sterile, are used in non-surgical settings. While not sterile, they effectively protect healthcare workers and prevent infection spread in general healthcare environments.
Packaging: Isolation Gown Vs Surgical Gown
Sterile Packaging:
- Surgical gowns are typically packaged individually in sterile conditions to maintain sterility until they are used. This is crucial because surgical gowns are used in environments where maintaining a sterile field is essential, such as in operating rooms and ICUs.
- Isolation gowns are usually packed in bulk, such as in packs of 5 or 10 pieces per PE (polyethylene) bag. This type of packaging is designed to be space-saving and cost-effective, making it easier to store and transport large quantities.
Packaging Materials:
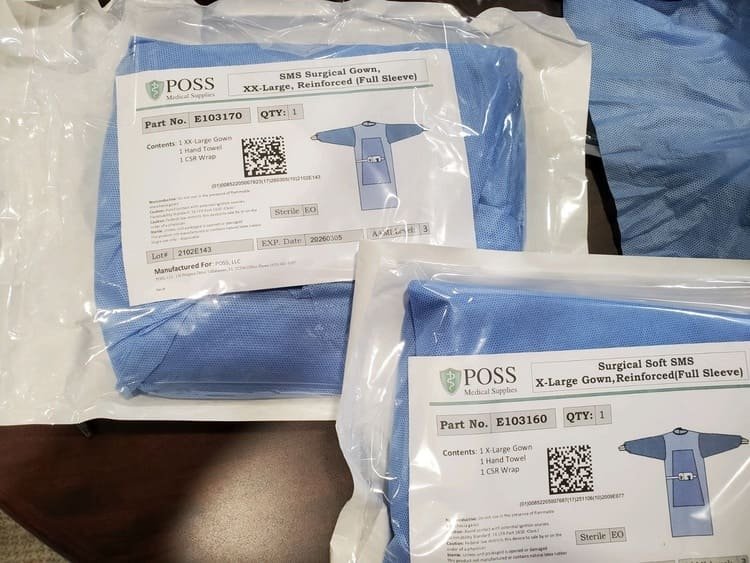

- The packaging of surgical gowns often consists of paper-poly bags, which have paper on one side (for labeling and product information) and plastic on the other side. This dual-material packaging helps ensure that the gown remains sterile while allowing for easy identification and handling. Each surgical gown package may include additional items like a hand towel or may be wrapped in SMS (spunbond-meltblown-spunbond) wrapping cloth, which further aids in maintaining sterility.
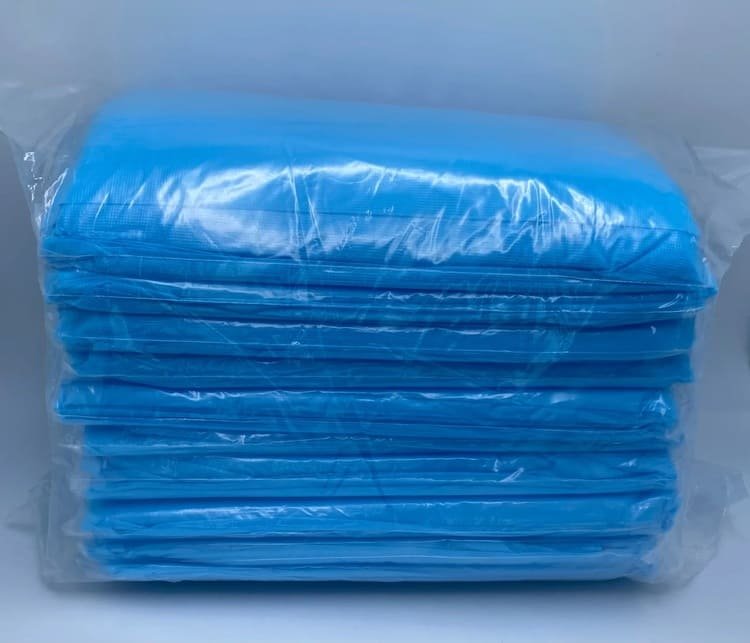

- Isolation gowns, on the other side, are usually packed in polyethylene bags, without sterilization. Isolation gowns are often vacuum-sealed to minimize package volume, which helps reduce shipping costs by removing excess air and compressing the gowns for easier storage and transport
Cost
Surgical gowns are generally more expensive due to several factors. They are made from high-grade materials like SMS or SMMS, feature reinforced critical zones, and undergo sterilization processes. Additionally, surgical gowns must meet rigorous AAMI Level 3 and 4 protection standards, requiring extensive testing and certification. These factors significantly increase manufacturing costs and overall prices.
In contrast, isolation gowns are more cost-effective. They typically use lighter, less expensive materials such as non-woven polypropylene or polyethylene, lack reinforced areas, and are usually non-sterile. Designed to meet lower protection standards (AAMI Levels 1-2, occasionally 3), isolation gowns require less rigorous testing. This results in lower production costs and makes them more economical for everyday use in lower-risk healthcare settings. The price difference is substantial, with isolation gowns often available at a fraction of the cost of surgical gowns.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Surgical Gowns | Isolation Gowns |
| Purpose | Moderate to high risk | Low to moderate risk |
| Material | SMS, SMMS, composite materials; with a higher fabric weight | Polypropylene, SMS, PE coated non-woven; much thinner. |
| Design | Snug fit, with 4 ties to ensure stability. Usually, the critical zones are reinforced. | Looser fit for ease of movement. |
| Protection Level | AAMI level 3 and 4 | AAMI level 1, 2, and sometimes 3 |
| Sterility | Provided sterile | Often non-sterile |
| Typical Cost | Higher | Lower |
In conclusion, understanding the differences between isolation gown vs surgical gown is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure proper protection in various medical scenarios. For medical gown wholesalers, distributors, and procurement staff in medical institutions, this knowledge is particularly valuable in making informed decisions about inventory management and supply chain optimization. By selecting the appropriate gowns based on the level of risk, material requirements, and specific healthcare settings, you can better meet the diverse needs of your clients or healthcare facilities while ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Contact Morntrip today for your medical gown needs! As a leading Chinese manufacturer, we offer expert guidance and OEM solutions for all types of medical gowns. Whether you’re a wholesaler, distributor, or procurement specialist, our competitive prices and excellent service will meet your requirements. Email info@morntrip.com now to discuss how we can improve your medical gown supply. Don’t delay – ensure top-quality protection for healthcare workers and patients with Morntrip’s gowns!






