Table of Contents
Disposable isolation gowns play a crucial role in protecting professionals across healthcare, cleaning, food processing, and laboratory settings. These essential garments are typically crafted from non-woven fabrics and plastic films that provide excellent barrier protection. The most common materials used include polypropylene, known for its lightweight and breathable properties; polyester, valued for its durability and chemical resistance; and polyethylene, prized for its waterproof qualities. Understanding the composition of these gowns reveals why they are far more than simple protective wear, but rather a vital component in maintaining rigorous safety and hygiene standards across various industries. (Sante Group, Henry Schein)

Overview of Disposable Isolation Gowns
Disposable isolation gowns are single-use protective garments crucial for shielding workers in healthcare, laboratory, and industrial settings from infectious agents and hazardous materials. They are classified into four levels based on protective capabilities, ranging from Level 1 for minimal risk situations to Level 4 for high-risk, fluid-intensive procedures.
- Level 1: Minimal risk, used during basic care and standard isolation.
- Level 2: Low risk, suitable for blood draws and suturing.
- Level 3: Moderate risk, ideal for arterial blood draws and inserting IVs.
- Level 4: High risk, designed for long, fluid-intensive procedures.
Primarily manufactured from non-woven fabrics or plastic materials, they balance protection with comfort. Non-woven fabrics offer breathability, while plastic materials provide superior fluid resistance. The choice of material depends on the specific environment and level of protection required. Whether in hospitals, labs, or hazardous industrial settings, disposable isolation gowns play a vital role in maintaining safety standards and preventing contamination.

What are Non Woven Isolation Gowns made of?
Non-woven fabrics have transformed healthcare, particularly in the production of disposable isolation gowns. Created by bonding fibers through chemical, mechanical, or thermal processes, these materials offer unique properties ideal for medical applications. Non-woven isolation gowns are lightweight, breathable, and water-resistant, striking an optimal balance between protection and comfort. A National Institutes of Health study revealed that non-woven fabrics can be up to 10 times more effective at filtration than traditional woven fabrics, providing crucial protection in healthcare settings. Their disposable nature also minimizes cross-contamination risks. In hospitals, where hygiene is paramount, these gowns serve as an indispensable shield against infection.

Polypropylene (PP) is a key material in the production of disposable isolation gowns. This lightweight yet durable synthetic polymer offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, moisture resistance, and flexibility. These properties make PP an ideal choice for medical applications where barrier protection and comfort are paramount.
The advantages of using PP in isolation gowns include:
- Cost-effectiveness: Affordable production, is crucial for budget-conscious healthcare facilities.
- Durability: Withstands high temperatures, enabling effective sterilization.
- Potential reusability: Can be sterilized for multiple uses, reducing environmental impact.
- Comfort: Flexibility and lightweight nature contribute to improved wearability.
- Enhanced performance: A study by the American Journal of Infection Control suggests comfortable PPE leads to better performance among healthcare professionals.
These factors combined make polypropylene an optimal material for disposable isolation gowns in medical settings.
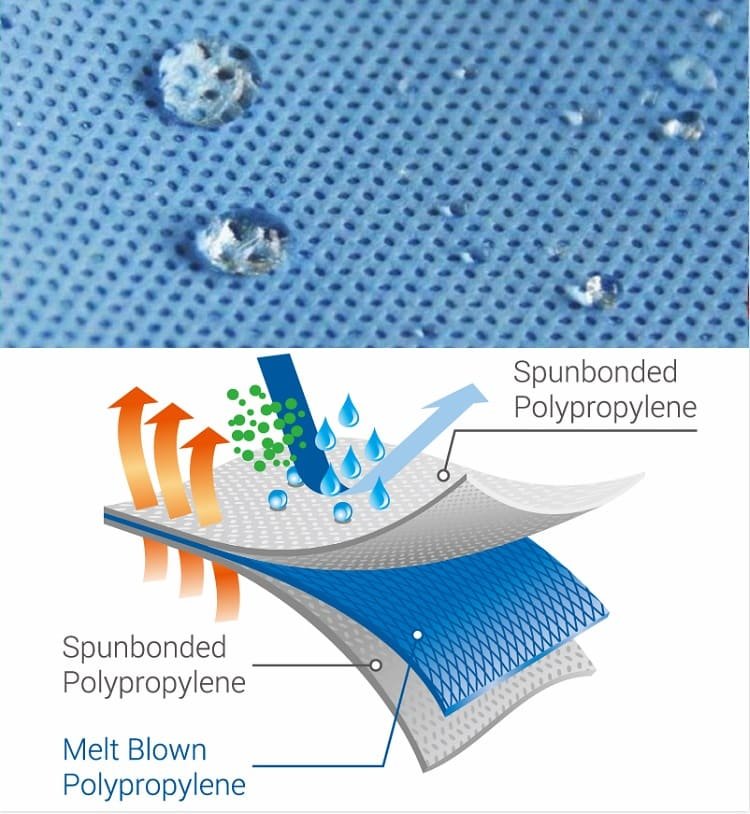
SMS (Spunbond–Meltblown-Spunbond) fabric is a crucial component in disposable isolation gowns. This non-woven material consists of three layers: two outer spun-bond polypropylene layers for strength and durability, and a middle melt-blown polypropylene layer for filtration. This unique structure results in a fabric that is both robust and breathable, making it ideal for medical applications.
The advantages of SMS fabric in isolation gowns include:
- Enhanced protection: The meltblown layer provides high filtration capacity, effectively blocking bacteria and viruses.
- Comfort: Spunbond layers offer softness and flexibility, ensuring wearability during extended use.
- Breathability: The fabric’s structure allows air circulation, reducing heat buildup.
- Cost-effectiveness: Relatively inexpensive to produce, making it suitable for high-volume use in healthcare settings.
- Balanced performance: Combines barrier protection with comfort, addressing key requirements for medical protective wear.
These properties make SMS fabric a preferred choice for disposable isolation gowns in healthcare environments.

PE-coated non-woven materials are a crucial innovation in disposable isolation gowns, combining the benefits of polypropylene (PP) or SMS fabrics with polyethylene (PE) coating. This combination enhances the gowns’ protective properties, particularly in terms of fluid resistance.
Key advantages of PE-coated isolation gowns include:
- Enhanced fluid resistance: The PE coating provides superior waterproofing.
- Balanced protection: Offers a combination of breathability and fluid resistance.
- Versatility: Suitable for environments with moderate fluid exposure, such as laboratories and pathology units.
- Comfort: Maintains breathability despite the additional protective layer.
- Durability: The PE coating adds strength to the underlying fabric.
Two popular variants are PP+PE and SMS+PE gowns. PP+PE gowns balance breathability with fluid resistance, while SMS+PE gowns combine the inherent strength of SMS fabric with enhanced fluid protection. These materials offer an optimal solution for medical and laboratory settings, ensuring both safety and comfort for wearers.
What are plastic isolation gowns made of?
Polyethylene
Polyethylene isolation gowns are a specialized type of disposable protective wear, primarily composed of polyethylene plastic. This material is chosen for its exceptional fluid resistance, making it ideal for high-risk environments where exposure to liquids is frequent and potentially hazardous.
Key features and applications of polyethylene gowns include:
- Superior fluid resistance: Provides an effective barrier against bodily fluids, chemicals, and other liquid contaminants.
- High-risk environment suitability: Ideal for use in hospitals, emergency rooms, and laboratories where fluid exposure is common.
- Enhanced safety: Offers reliable protection, allowing healthcare workers to focus on their tasks without compromising safety.
- Disposability: Single-use nature reduces risk of cross-contamination.
- Barrier effectiveness: Acts as a critical shield against potential contaminants in medical settings.
These gowns are particularly valuable in scenarios requiring maximum protection against fluid-borne hazards, ensuring a safer working environment for medical professionals in high-risk situations.

CPE
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) is a premium material used in high-performance disposable isolation gowns. These gowns are designed to provide superior protection in healthcare and industrial settings where fluid resistance is paramount.
Key features and benefits of CPE gowns include:
- Exceptional fluid resistance: CPE offers superior protection against spills, splashes, and contaminants.
- Comprehensive coverage: Designed to shield from neck to knees, ensuring extensive bodily protection.
- Secure fit: Equipped with ties and thumb loops for a snug, stable fit during use.
- Enhanced safety: Provides a reliable barrier against hazardous materials and contaminants.
- Versatility: Suitable for both healthcare and industrial environments requiring high-level protection.
The combination of CPE’s fluid-resistant properties and the gown’s design features, such as secure fastenings and extended coverage, make these isolation gowns an excellent choice for scenarios demanding maximum protection. This comprehensive approach to safety allows workers to perform their duties with confidence in high-risk environments.
Comparison Table of Isolation Gown Materials
| Material | Protection Level | Breathability | ANSI/AAMI Level | Use Cases |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Basic | High | Level 1 | Conventional isolation |
| SMS | Moderate to High | Moderate | Level 1-3 | General medical use, OR gowns |
| PP+PE | High | Low | Level 1-2 | Waterproofing needs |
| SMS+PE | Very High | Low | Up to Level 3 | High fluid exposure |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Very High | Low | Varies | Chemical resistance |
| CPE | Very High | Low | Level 2-3 | Chemical and fluid protection |
Disposable isolation gowns are essential in healthcare settings, with materials playing a crucial role in their effectiveness. From lightweight polypropylene for low-risk environments to SMS fabrics for moderate protection, and polyethylene-coated gowns for high-risk scenarios, each material offers unique benefits. Non-woven, SMS, PE-coated, and specialized polyethylene gowns cater to varying needs, balancing protection, comfort, and breathability. The choice of gown depends on the specific risk level and environment, with factors like fluid resistance, durability, and comfort guiding the selection process. Understanding these materials and their applications is vital for ensuring the safety of healthcare professionals and patients alike, allowing for informed decisions that match protective qualities to specific risks present in different medical settings.
As a leading manufacturer of disposable isolation gowns, Morntrip is always here to support your protective wear needs. Contact info@morntrip.com today for expert guidance on choosing the right gowns for your specific requirements. From non-woven to PE-coated options, we offer a comprehensive range of high-quality isolation gowns. Let us help you ensure optimal protection for your healthcare environment.






