Table of Contents
Medical gowns play a vital role in healthcare, protecting both workers and patients. They act as a barrier against infections, ensuring safety and reducing contamination risks. However, the effectiveness of these gowns depends heavily on the materials used. (FDA)
Different types of gowns serve specific purposes. Disposable gowns, often made from Polypropylene, are lightweight and convenient for single use. In contrast, reusable gowns, such as those made from cotton-poly blends, offer greater durability but require proper laundering to maintain their protective qualities.
Each material has its advantages and challenges. Polypropylene provides excellent protection against fluids but may sacrifice comfort during long shifts. Cotton-poly blends feel more breathable and comfortable but might not offer the same fluid resistance. Selecting the right type involves balancing safety, comfort, and practicality.
Understanding these differences ensures informed decisions for healthcare administrators and procurement teams. Choosing the right gown material can protect healthcare staff, improve patient care, and manage resources effectively.

What Are Medical Gowns?
Medical Gown Definition
Medical gowns are protective clothing for healthcare workers, designed to shield them and others from infections, especially during procedures involving exposure to bodily fluids or other contaminants.
These gowns act as a barrier, preventing infectious droplets, microorganisms, and particles from contacting the wearer’s skin and clothes. Primarily intended for single use, they come in various styles and materials to suit different clinical settings and risk levels. The FDA categorizes these gowns as personal protective equipment (PPE), emphasizing their critical role in ensuring safety in medical environments.
What are medical gowns used for?
Medical gowns are vital for infection control in healthcare settings. They protect healthcare workers from direct exposure to potentially infectious agents, helping stop the spread of diseases between patients and staff. Using gowns aligns with strict regulatory standards, aimed at maintaining a safe environment for both patients and medical staff. By acting as a barrier against contaminants, these gowns reduce the risk of cross-contamination and are essential in settings like hospitals, clinics, and labs where infection control is crucial.
Overview of Different Types
Medical gowns come in various types, each designed for specific purposes.
-
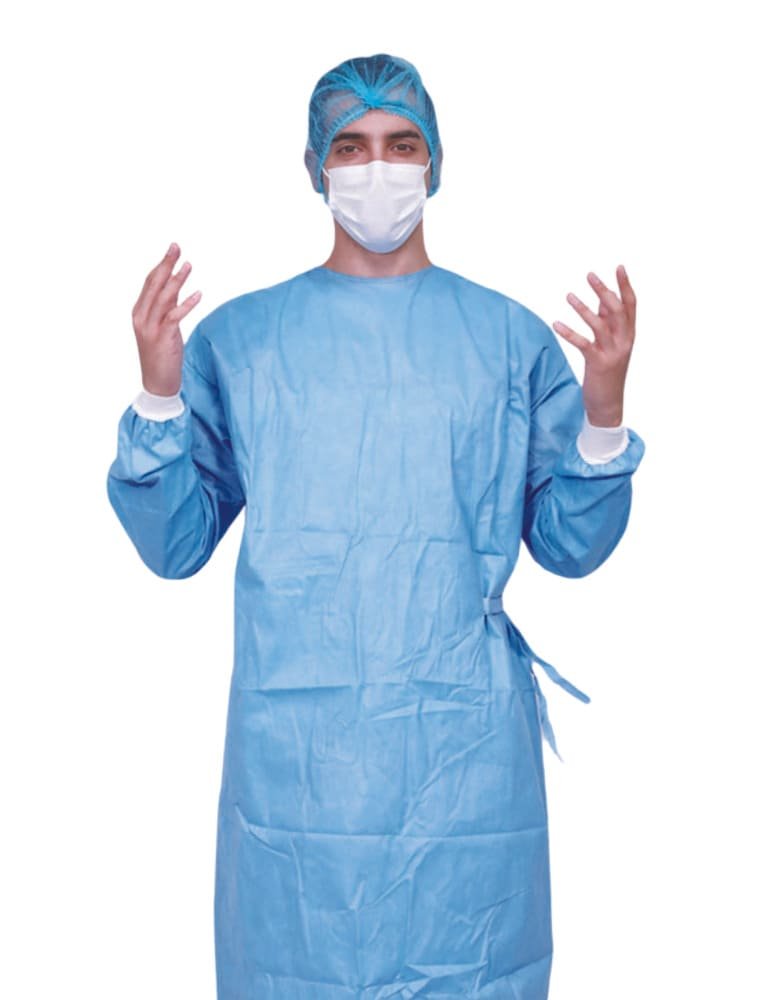
Surgical Gowns provide high protection for surgeries and procedures with a high risk of fluid exposure, covering key areas like the front, sleeves, and back, making them ideal for operating rooms. Usually, Surgical Gowns are made of more heavy weight fabrics than isolation gowns.
-
Surgical isolation gowns offer even more coverage, protecting against infectious materials in high-risk situations.
-
Non-surgical isolation gowns are popular to be worn in less intense settings, for offering a basic barrier against light fluid contact, though they’re not suitable for high-risk or invasive procedures. Although this is not quite accurate, in many cases, non-surgical isolation gowns are often referred to simply as isolation gowns.
-
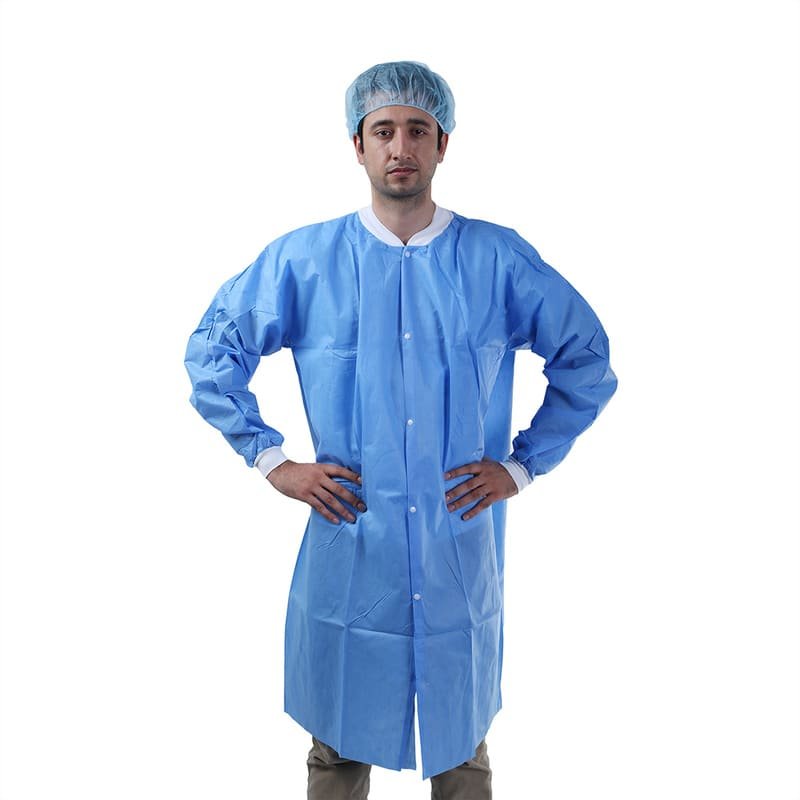
Lab Coats serve as a practical option for everyday protection in clinical and lab settings but aren’t made for use in situations involving heavy fluid exposure.
4 Levels of Medical Gowns
Medical gowns are rated in four levels based on their barrier protection, from Level 1 to Level 4.
-
Level 1 gowns suit minimal-risk environments, like basic care and standard isolation, and provide limited fluid protection.
-
Level 2 gowns offer moderate barrier protection, useful in cases with low fluid exposure, such as blood draws or ICU care.
-
Level 3 gowns have higher fluid resistance, ideal for more intense situations like arterial blood draws or trauma care, where fluid exposure risk is moderate to high.
-
Level 4 gowns are the highest level, for high-risk environments, including surgeries and procedures with exposure to pathogens, as they provide maximum protection against fluids and microbes. Each level addresses specific needs in healthcare, ensuring the safety of both healthcare professionals and patients.
What Are Medical Gowns Made Of?

Polyester
Polyester is a strong, synthetic fabric known for resisting spills and wear. Its tight weave makes it ideal for reusable gowns that undergo frequent washing and high temperatures. Polyester keeps its shape and color even after many sterilizations and resists wrinkles. This makes it suitable for healthcare settings where durability and consistent appearance are essential.

Cotton
Cotton is appreciated for its comfort and breathability, making it ideal for long wear in healthcare. This natural fiber promotes airflow, reducing sweat and discomfort—an advantage for Lab Coats or specific Surgical Gowns. Its softness benefits both patients and staff, adding comfort. Although less resistant to liquids than synthetics, cotton balances comfort and utility well.

Polypropylene
Polypropylene is a lightweight, breathable, and affordable choice commonly used for disposable gowns, especially isolation gowns. It provides a solid barrier against contaminants without adding bulk. Its affordability makes it popular for single-use gowns, keeping costs down while still offering effective protection.

SMS Fabric (Spunbond Meltblown Spunbond)
SMS fabric, a nonwoven blend of spunbond and meltblown Polypropylene layers, offers strong fluid resistance and breathability. This makes it ideal for disposable surgical gowns, creating a barrier against fluids while allowing airflow. Light and flexible, SMS fabric is comfortable for extended wear and meets high protection standards, especially in disposable isolation gowns for high-level procedures.
SMMS / SMMMS (Spunbond, Meltblown, Meltblown, Spunbond)
SMMS and SMMMS fabrics feature a four-layer structure for added protection over SMS fabric. They consist of two outer layers of spunbond Polypropylene with 2-3 inner meltblown layers, providing a robust barrier against fluids and contaminants. Gowns made from SMMS or SMMMS often meet ANSI/AAMI Level 2-4 standards, suitable for high-protection environments while maintaining breathability.

PE Coated Fabrics (PP+PE or SMS+PE)
PE-coated fabrics combine Polypropylene with a polyethylene layer, making these gowns lightweight and waterproof. The PE coating adds fluid resistance, ideal for low-risk settings needing splash protection. Despite their lightweight design, these gowns offer basic protection, making them practical for less intensive healthcare applications.

Wood Pulp Spunlace Fabric: Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Choice
Wood pulp spunlace fabric offers an eco-friendly option for disposable medical gowns, made from biodegradable wood pulp. This material has a soft, cloth-like feel, combining comfort with good splash resistance and breathability. Non-toxic and fully degradable, it supports sustainability goals. Although slightly pricier than some alternatives, wood pulp spunlace gowns are valued for their mix of comfort, safety, and environmental responsibility.
Key Differences Between Medical Gowns and Hospital Gowns
Medical gowns and hospital gowns are terms that often overlap but refer to different types of garments used in healthcare settings.
Definitions

Hospital Gowns
-
Description: Hospital gowns, also known as patient gowns or “johnny gowns,” are typically worn by patients during their stay in a medical facility. They are designed for easy access to the patient’s body for examinations and procedures.
-
Material: These gowns can be made from cotton or disposable materials and often feature ties at the back to ensure modesty while allowing medical staff to perform their duties easily.
Medical Gowns
-
Description: Medical gowns refer more broadly to garments used by healthcare professionals as personal protective equipment (PPE). These include Surgical Gowns, isolation gowns, and procedural gowns designed to protect both the wearer and the patient from contamination.
-
Purpose: Medical gowns are intended to provide a barrier against infectious materials and are regulated by standards that specify their protective capabilities. They are classified based on the level of protection they offer, which can vary from minimal to high risk depending on the situation.
Key Differences
|
Feature |
Hospital Gowns |
Medical Gowns |
|
Primary Users |
Patients |
Healthcare professionals |
|
Design Purpose |
Comfort and accessibility for exams |
Protection against infection and contamination |
|
Material |
Cotton or disposable |
Varies; often more robust materials |
|
Regulation |
Generally not regulated |
Regulated as Medical devices by the FDA |
|
Types |
Standard patient gown |
Surgical, isolation, procedural gowns |
In summary, while hospital gowns are specifically designed for patients, medical gowns encompass a wider range of protective garments used by healthcare workers. Thus, they are not synonymous but rather part of a broader classification within medical apparel.
How to Choose the Right Medical Gown Material
Selecting the right medical gown material is essential for its effectiveness, durability, and the wearer’s comfort. Here are key factors to consider:
Purpose or Usage Scenario
The gown’s intended purpose largely determines the material choice. For high-risk surgeries, choose fluid-resistant and barrier materials like polyethylene or SMS (spunbond-meltblown-spunbond) fabric, which offer strong protection against pathogens. For lower-risk settings, such as routine check-ups, a lighter, breathable material like non-woven Polypropylene works well.
Cost-effectiveness and Durability
Material costs and durability vary. Single-use gowns made of Polypropylene can be a cost-effective, hygienic option. In contrast, reusable gowns crafted from woven fabrics with chemical coatings provide long-lasting use, making them ideal for facilities focused on sustainability and waste reduction.
User Comfort and Wearer Experience
Comfort is crucial for healthcare workers who may wear gowns for hours. Breathable fabrics like SMS balance protection with airflow, reducing heat and moisture buildup. Soft, skin-friendly materials are best for those with sensitive skin, as comfort aids focus and productivity during long shifts.
Choosing the right material is key when selecting medical gowns. The right fabric means effective protection, while the wrong choice could compromise safety in high-risk settings. High-quality, well-suited fabrics provide enhanced protection, comfort, and durability, directly benefiting both patients and healthcare workers.
If you’re looking for medical gowns or need assistance in selecting the best fabric, consider working with an experienced supplier. With over 20 years as a leading medical gown manufacturer in China, we bring quality and expertise to every gown. Reach out for guidance or to explore reliable medical gown solutions tailored to your needs.







